What is Neurology
What are the roles of the nervous system and how can it impact our daily living

What is Neurology?
Neurology is the branch of medicine focussed on the body’s nervous system which includes the brain, spinal cord and nerves. The nervous system is composed of various neural networks where signalling between these networks enables the body to think, feel, learn, memorise, language, sensation and functioning.
Research has strongly-established the existing cells within the nervous system to have the ability to adapt to unencountered situations, damage, disease or injury through creating neural pathways; the term is plasticity.
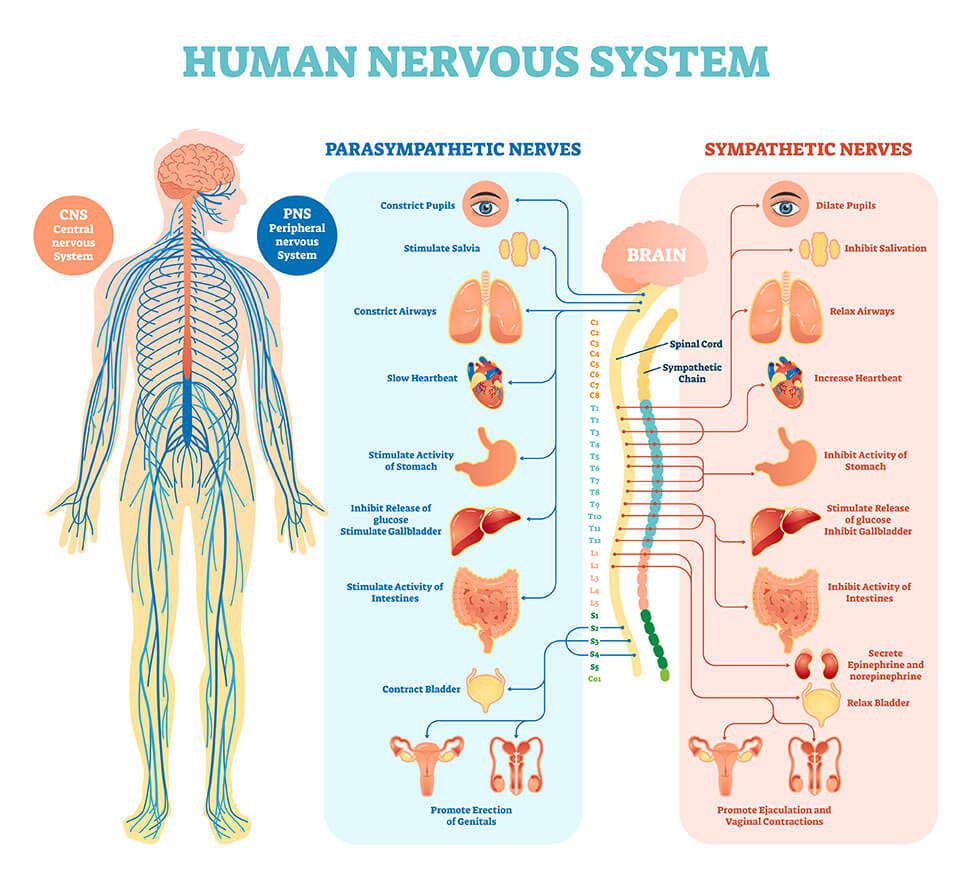
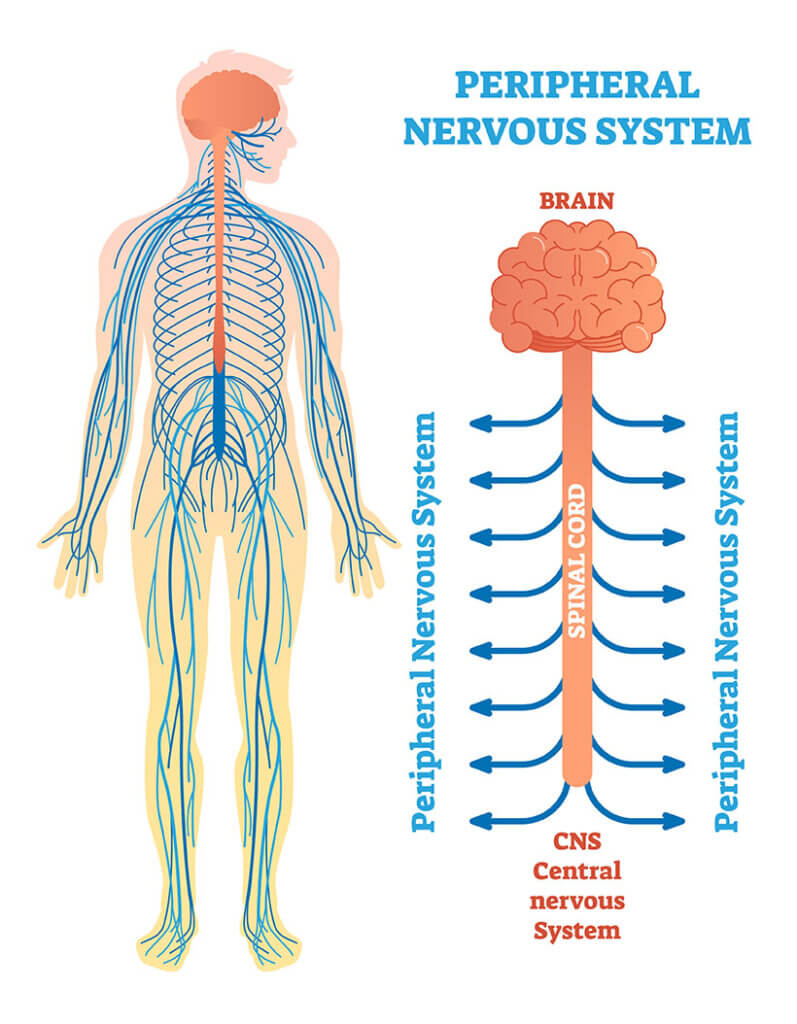
The nervous system can be separated into two systems: the central nervous system [CNS] and peripheral nervous system [PNS].
The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain’s role is to receive and process information to initiate responses, store and memorise information, and generate emotions and thoughts. The spinal cord can be viewed as the highway from the brain to the sensors within the peripheral body with the role of transmitting information both ways and controlling reflexes.
As for the Peripheral Nervous System, it consists of two subtypes, the Autonomic Nervous System and the Somatic Nervous System. The ANS is responsible for the autonomic regulation of involuntary bodily functions such as respiration, circulation, metabolism, secretion, body temperature and reproduction.
This system is further categorised into two divisions: the Parasympathetic and Sympathetic.
The parasympathetic division is also known as the “rest and digest” response. It has the ability and role to decrease the force of cardiac muscle, reduce heart rate, decrease the size of respiratory branches [bronchoconstriction], increase mucous secretion, increase peristalsis [wave-like movement of the oesophagus to allow food to travel from the mouth to stomach], and increase glandular secretions.
The sympathetic division is described as the “flight or fight” response. This system prepares the body to respond to a stressful stimulus. It has the ability to cause the muscle within the blood vessels to contract [vasoconstriction] consequently increasing heart rate and blood pressure; allowing more blood to flow to muscles for action.
The Somatic Nervous System is responsible for the voluntary control of movements by transmitting sensory and motor information to and from the central nervous system. Cranial and Spinal Nerves are the primary contributors to the Somatic Nervous System as they provide voluntary motor control and sensation to/from the face, head, trunk and limbs.
Maddi Law – Exercise Physiologist
